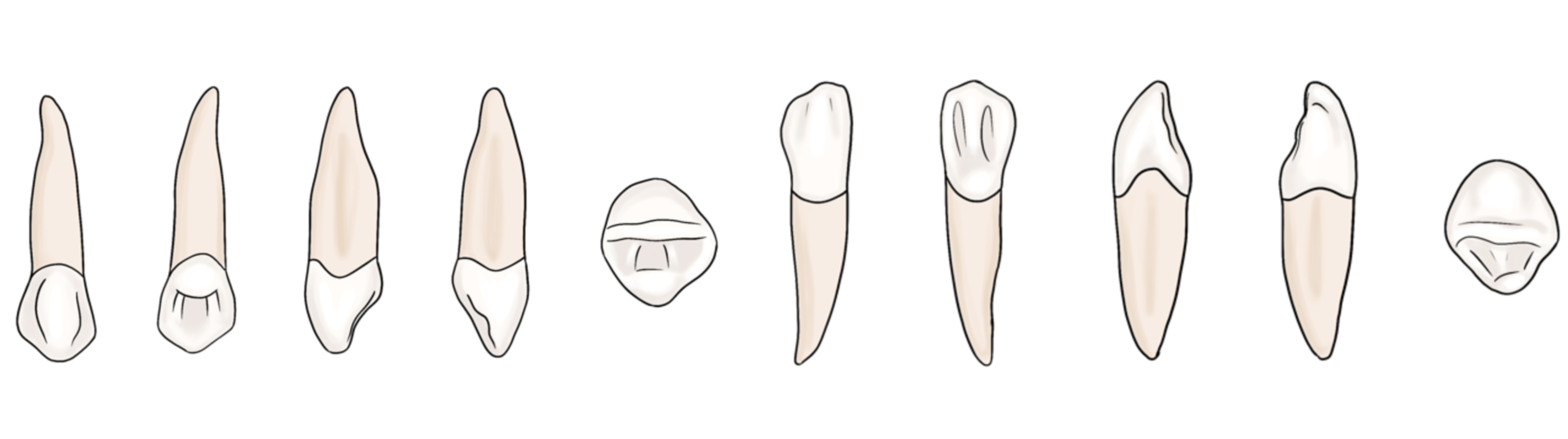
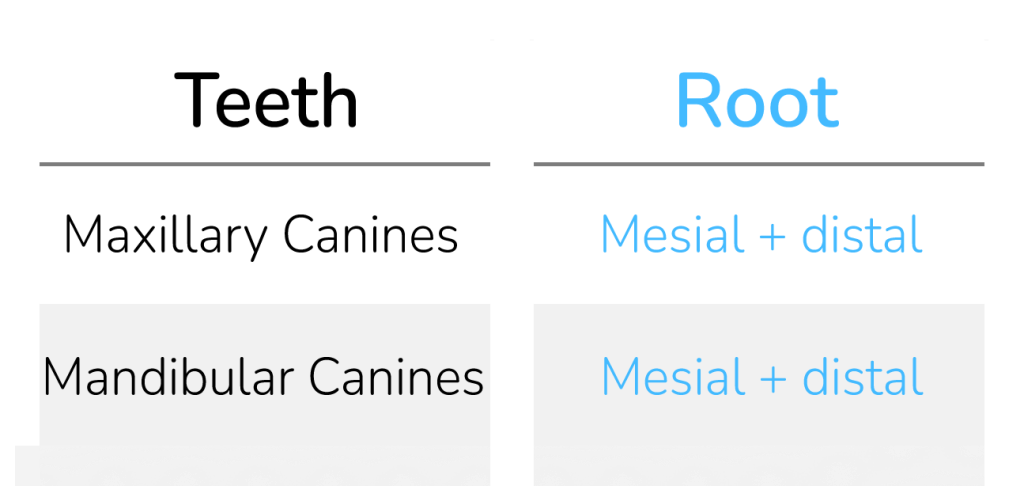
Canines
#6, 11, 22, 27
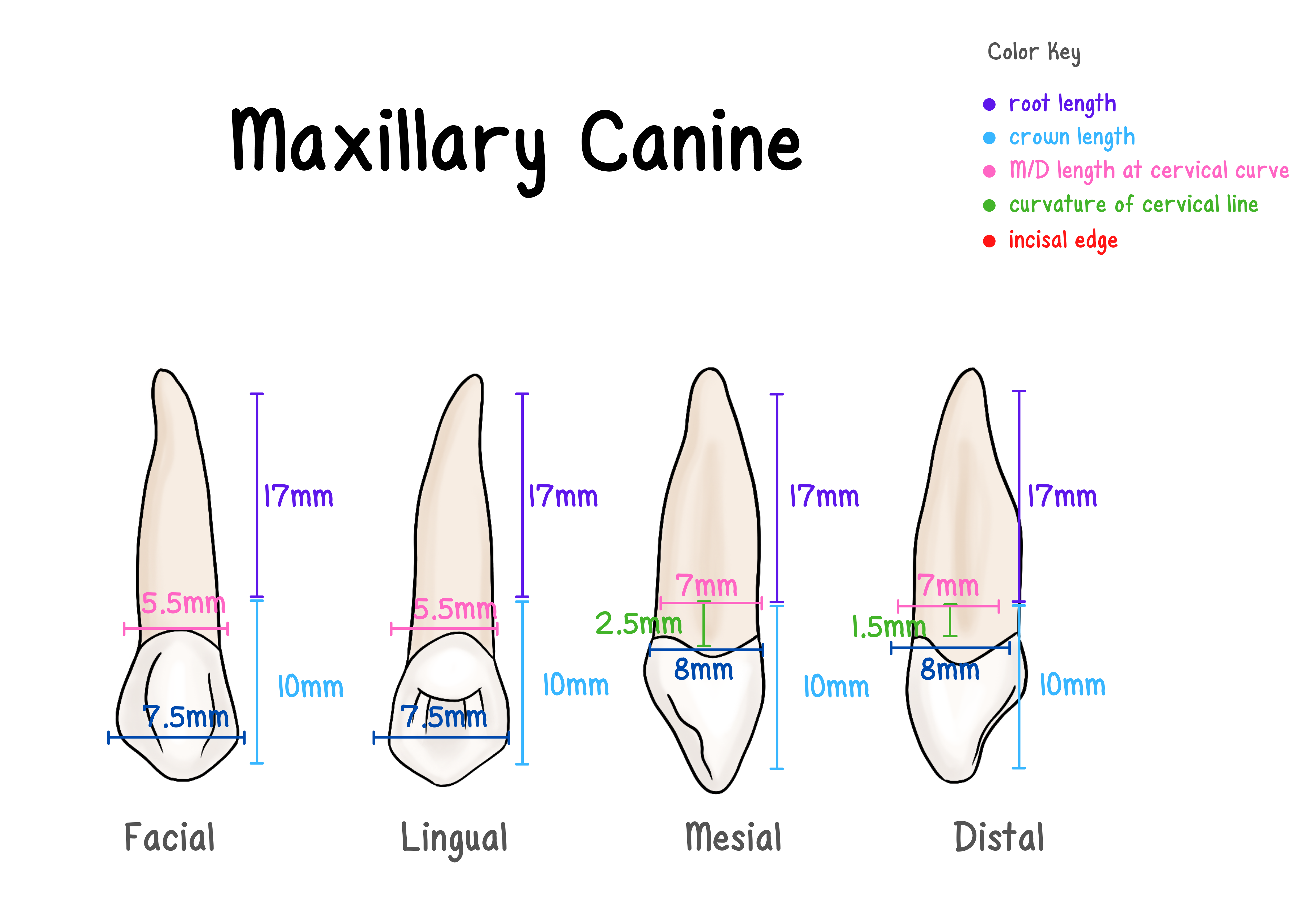
Maxillary Canine
Video failed to load. Please try again.

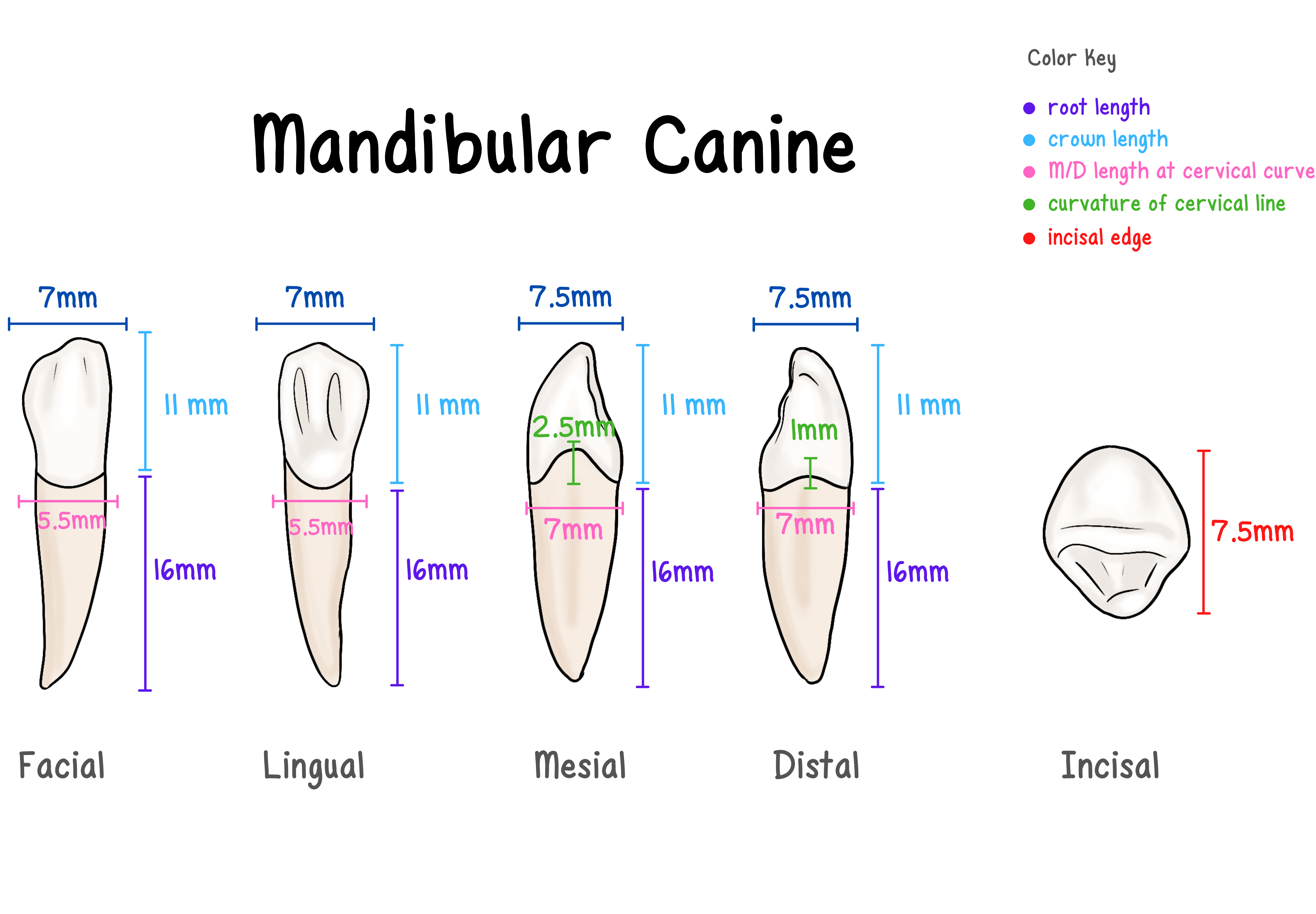
Mandibular Canine
Video failed to load. Please try again.

Measurements
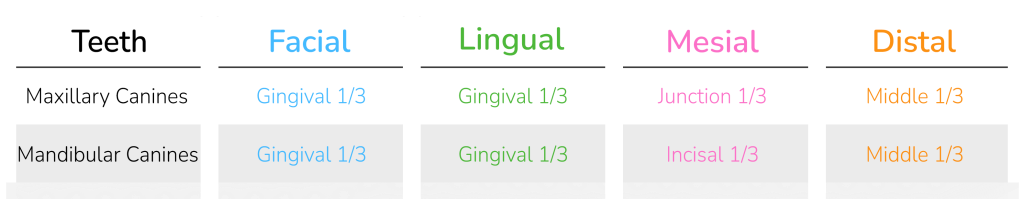
Height of Contour
Root Depressions
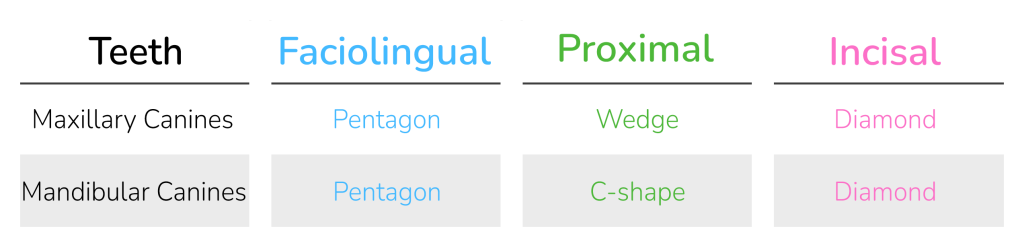
Crown Shapes
Eruption and Calcification

Quiz Time!
Test your knowledge of this chapter by completing the following questions
Learn More Anatomy
References
Nelson. (2009). Wheeler’s Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion (9th ed.). Elsevier.
Scheid, Weiss, G., & Woelfel, J. B. (2012). Woelfel’s dental anatomy (8th ed.). Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
